 By Independent News Roundup
By Independent News Roundup
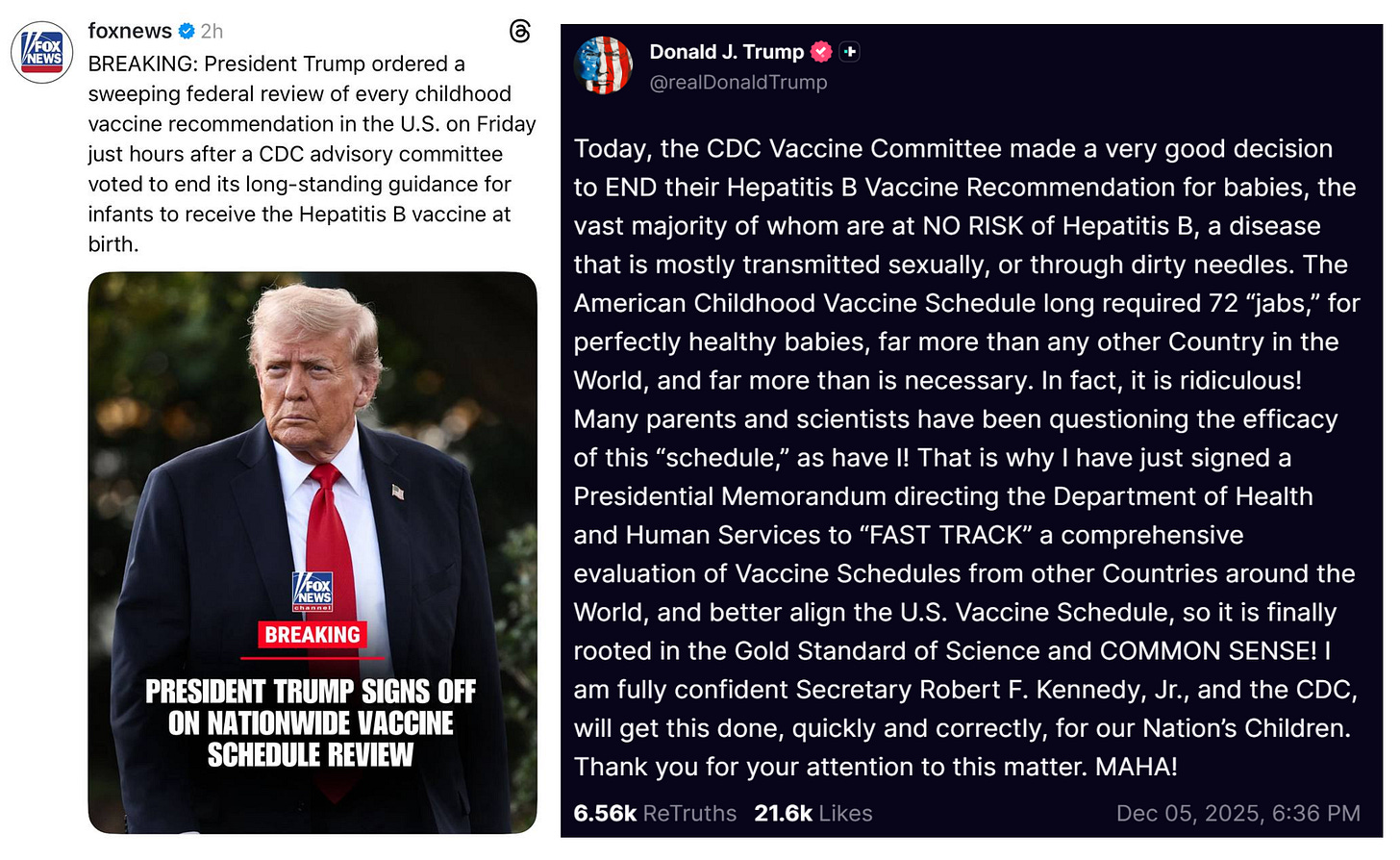
After the CDC ACIP panel voted 8-3 to drop the hepatitis B vaccine for millions of healthy babies born from seronegative mothers, President Trump who has previously said the ACIP schedule is a “disgrace” has ordered a review of the US vaccine schedule in relationship to the countries. Alter AI assisted in this review.
Based on the 2025 immunization schedules published by health authorities worldwide — including the CDC/ACIP (U.S.), Public Health England/UKHSA, Health Canada, Australia’s Department of Health, and the EU’s national public health programs — there are significant differences in how intensively children are vaccinated from birth to age 18.
Although all developed countries recommend broadly similar vaccines (targeting diphtheria, measles, polio, etc.), the United States stands at the top in total injections and doses, followed by Canada, France/Germany, the UK, Australia, Sweden, and Japan.
The 2025 CDC/ACIP schedule (see CDC PDF schedule, 2025) remains the most aggressive among Western nations.
By age one, a typical American baby receives 20+ doses spanning nine diseases (Hepatitis B, Rotavirus, DTaP, Hib, Pneumococcal, Polio, COVID‑19, Influenza, RSV). By age two, 32 individual antigens including monoclonal antibodies have been received in utero and after birth.
By age six, most children have accumulated around 27 to 29 doses, and around 30–32 total doses by age 18 (including HPV, meningococcal, Tdap boosters, annual flu shots, and now COVID boosters). Doses include combination products, so the number of antigens is much greater approximately 72-93 depending on maternal injections and other factors.
The U.S. uniquely begins vaccination at birth with Hepatitis B (now restricted to ~25,000 seropositive/carrier mothers) and adds multiple annual vaccines regardless of local exposure risk. It also promotes simultaneous injection of up to six vaccines at once (“combination vaccines” or same-visit stacking), magnifying early childhood exposure to adjuvants and preservatives.
Canada’s national and provincial schedules (see Health Canada)
mirror the U.S., but some provinces delay or skip optional vaccines
(like flu or COVID‑19 for healthy children). Fewer boosters are required
for diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis after age seven, and not all provinces
include HPV for boys.
Canada therefore averages 2–4 fewer total doses than the United States.
European Union countries vary widely:
European nations also tend to delay vaccination start ages to 8–12 weeks instead of giving Hep B or other shots at birth, resulting in fewer injections during infancy and more gradual immune stimulation.
The UK’s NHS and UKHSA recommend a smaller, slower schedule than North America’s. Infants receive about 16–18 doses by age 5, increasing to 20–21 by age 18.
Notably:
Australia’s National Immunisation Program (NIP) mirrors the UK more closely than the U.S.
Infants
start at 6–8 weeks, not at birth (Hep B exception). Only one influenza
vaccine per year is recommended, and chickenpox is given later. No
universal COVID vaccine for healthy under‑5s.
Total injections: about 20 by adulthood.
Nordic countries follow some of the world’s most minimalist Western schedules:
Children typically receive around 16–18 total injections before 18 — roughly half the U.S. burden — without suffering higher rates of “vaccine‑preventable” illness, challenging the dogma that more vaccines equal better outcomes.
Historically
the most cautious industrialized nation, Japan delayed and later
reduced its vaccine schedule after serious adverse events in the 1990s.
Although
it now recommends many standard vaccines, lower frequency,
single-antigen use, and minimal early‑life stacking mean the total doses remain lowest in the developed world, around 14–16 through adolescence.
Japan’s
infant mortality and autism rates are lower than in the U.S., prompting
renewed scientific interest in whether slower schedules might lower
iatrogenic risk.
Rank Country Approx. cumulative doses Notes on schedule intensity 1 🇺🇸 United States 30–32 Most intensive; starts at birth; annual flu + COVID 2 🇨🇦 Canada 25–28 Slightly milder than U.S.; fewer mandatory boosters 3 🇫🇷 France / 🇩🇪 Germany 22–25 Similar core vaccines; delayed start; selective flu use 4 🇬🇧 United Kingdom 20–21 No varicella or universal flu/COVID; efficient combinations 5 🇦🇺 Australia ≈ 20 Spaced schedule; limited COVID coverage 6 🇸🇪 Sweden / 🇳🇴 Norway 16–18 Simplified; no birth or seasonal routine vaccines 7 🇯🇵 Japan 14–16 Most delayed; minimal birth and combination doses
The data show a clear gradient: the United States vaccinates children more frequently and at earlier ages than any other Western nation, often stacking combinations before immune maturity. Nations with slower, smaller schedules — Sweden and Japan most notably — maintain equal or superior child health metrics, casting doubt on the premise that maximal dosing guarantees better outcomes.
The U.S. model prioritizes population‑wide compliance and theoretical herd immunity, while Europe and Japan incorporate a more individualized risk‑based approach. Given the expanding scientific literature on rising childhood allergic and neuropsychiatric illnesses, these cross‑national differences underscore the need for independent, transparent studies comparing long‑term health outcomes by cumulative vaccine burden — something major regulatory agencies have conspicuously avoided.
