 By Independent News Roundup
By Independent News Roundup
For years, public health agencies and pharmaceutical companies insisted it was “impossible” for COVID-19 mRNA injections to alter human DNA. They dismissed all concerns as “misinformation,” offering no evidence to back their assurances.
Today, that narrative collapses.
In our sentinel case report, Genomic Integration and Molecular Dysregulation in Aggressive Stage IV Bladder Cancer Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination (Dr. John A. Catanzaro, Nicolas Hulscher, and Dr. Peter A. McCullough; a Neo7Bioscience–McCullough Foundation collaboration), we document—for the first time—direct molecular evidence that genetic material from a COVID-19 mRNA “vaccine” has integrated into the human genome.
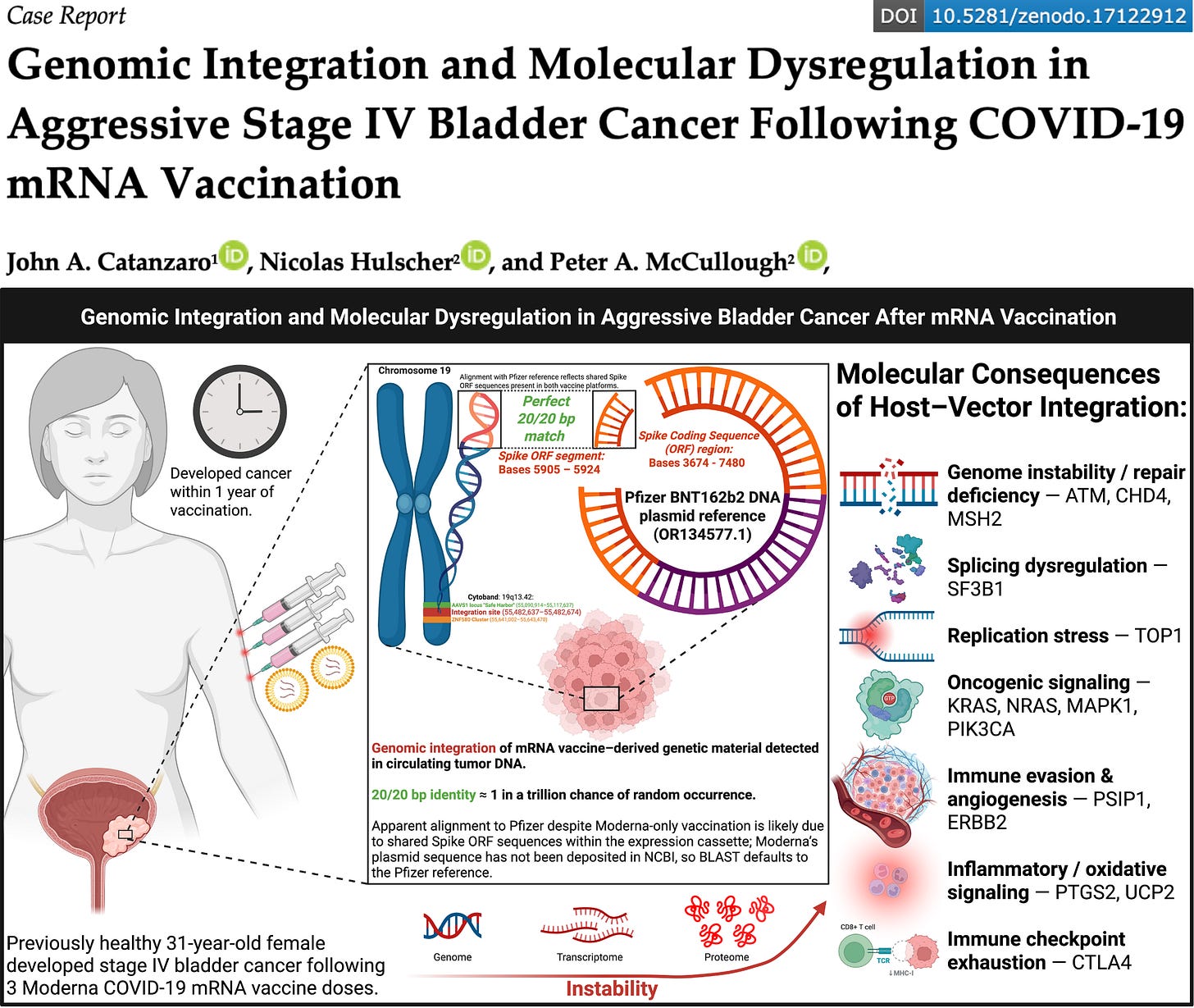
We describe a previously healthy 31-year-old woman who developed rapidly progressive stage IV bladder cancer within 12 months of completing a three-dose Moderna mRNA injection series. Bladder cancer is exceedingly rare in young women, and such aggressive presentations are almost unheard of.
To investigate, we performed comprehensive multi-omic profiling, including plasma-derived circulating tumor DNA, whole-blood RNA, and urine exosome proteomics. What we uncovered was striking:
Although the patient received only Moderna injections, the sequence aligned to Pfizer’s published BNT162b2 plasmid reference because Moderna has never deposited its proprietary plasmid in NCBI. Crucially, both Pfizer and Moderna vaccines encode the same prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein and therefore share identical stretches of nucleotide sequence within the Spike ORF coding region. It is within one of these conserved regions that the integration was captured, producing the perfect 20/20 bp match to the Pfizer reference.
The integration site was outside the canonical AAVS1 “safe harbor” locus ( ~55.09–55.12 Mb, 19q13.42) and instead mapped to chr19:55,482,637–55,482,674 (GRCh38), also within cytoband 19q13.42, positioned ~367 kb downstream of AAVS1 and ~158 kb upstream of ZNF580 at the proximal edge of the zinc-finger (ZNF) gene cluster. This region is gene-dense, transcriptionally active, and recombination-prone, with nearby regulators including ZNF580 (19q13.42) and ZNF582 (19q13.43). Integration in this unstable genomic context raises concern for transcriptional disruption, fusion transcript formation, and oncogenic potential.
The probability of a random 20-base sequence perfectly matching a predefined target is ~1 in a trillion. This makes accidental artifact virtually impossible.
Combined with the temporal proximity to vaccination, multi-omic evidence of oncogenic signaling, and direct genomic integration, the case establishes a biologically plausible pathway by which synthetic mRNA vaccines could contribute to cancer development.
Integration of vaccine-derived DNA or reverse-transcribed RNA into host chromosomes can occur through several known molecular routes:
All are biologically feasible and align with the patient’s detected DNA repair deficiencies (ATM, MSH2), which increase susceptibility to insertional mutagenesis. Notably, Speicher et al. quantified billions of residual plasmid DNA fragments per mRNA vaccine dose, exceeding regulatory safety limits by 36–627-fold, providing a plausible source of template DNA for genomic integration.

Nicolas Hulscher, MPH·7 SeptRead full story
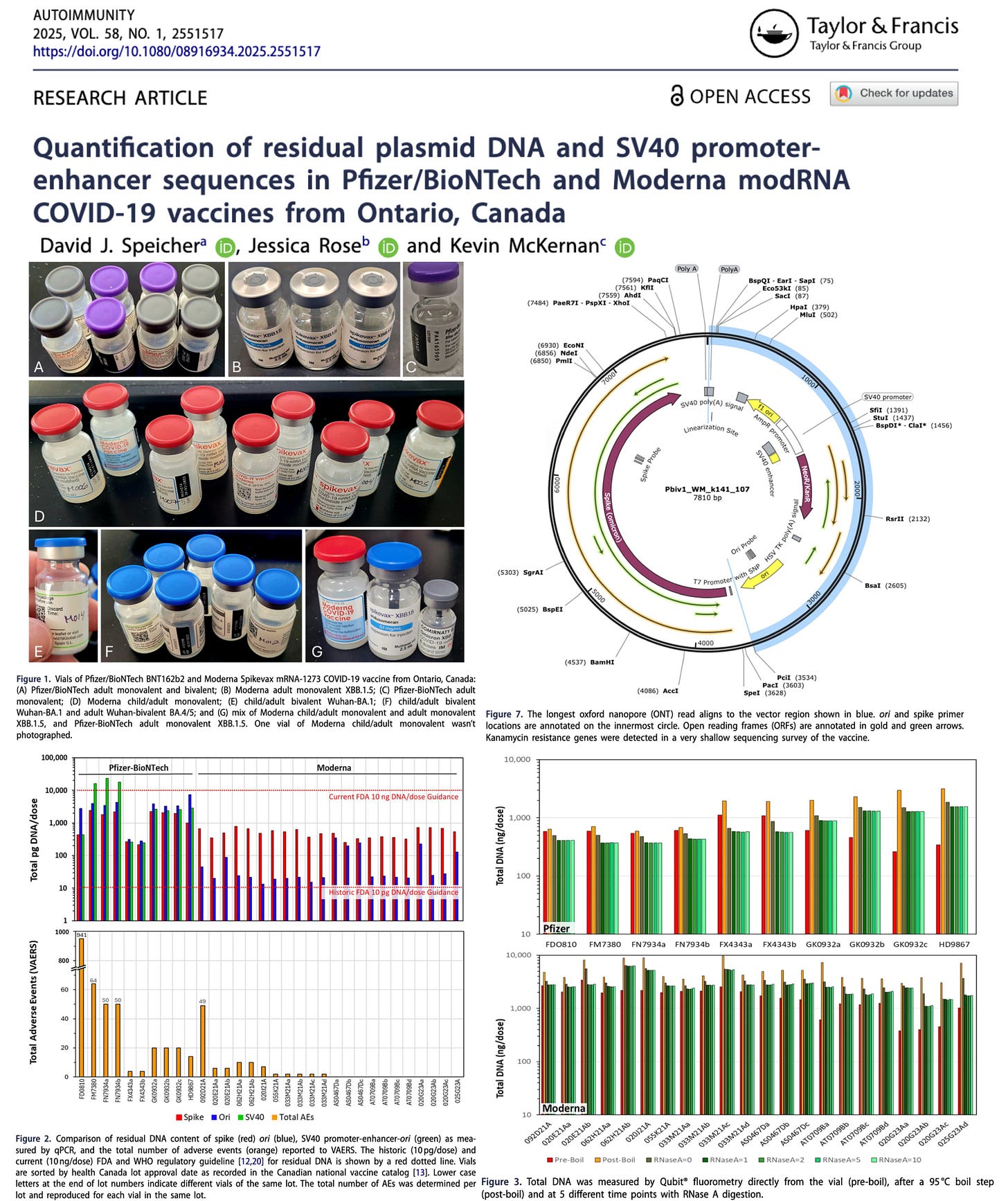
This sentinel case provides a critical mechanistic link in the mounting evidence that mRNA technology is carcinogenic.
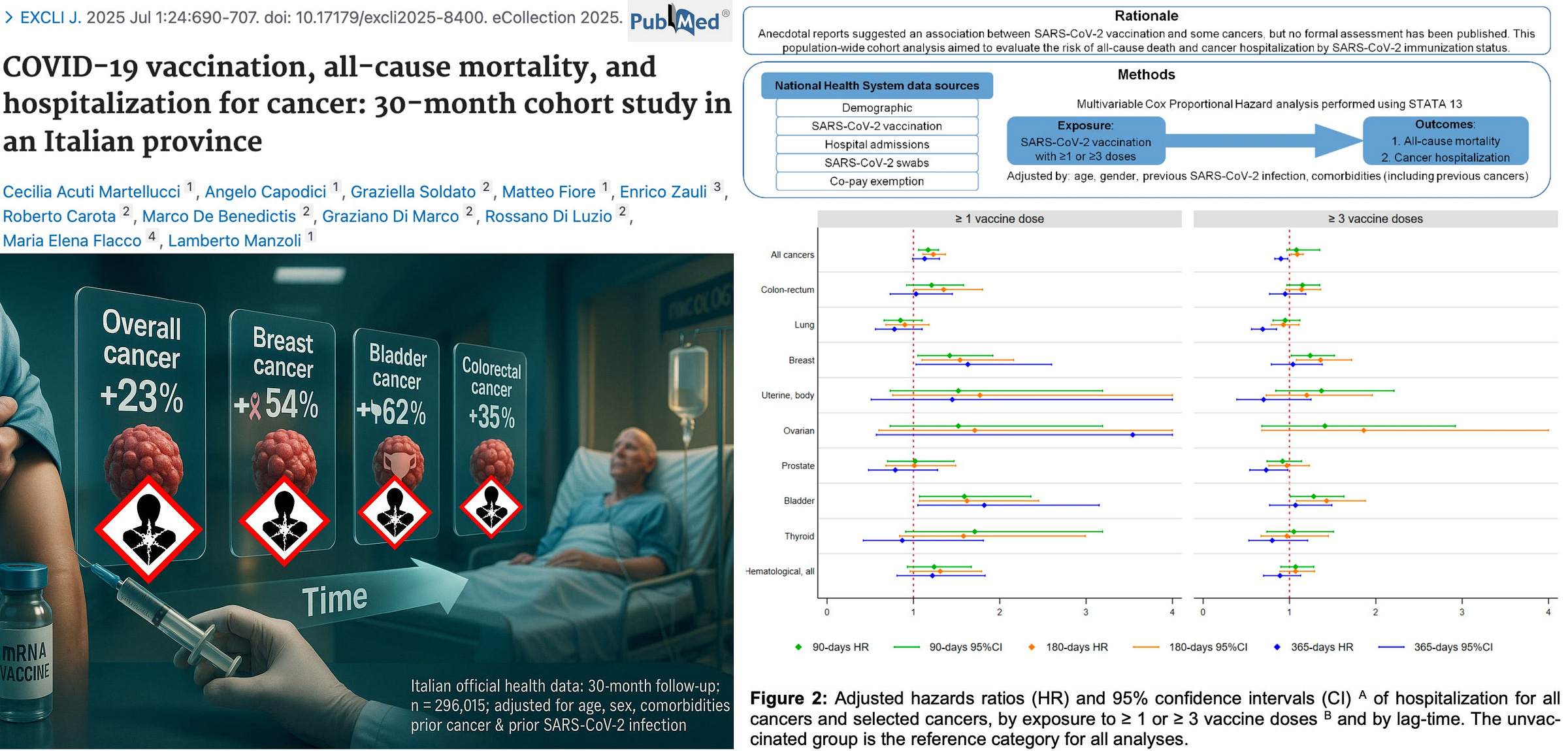

Nicolas Hulscher, MPH·31 AugRead full story
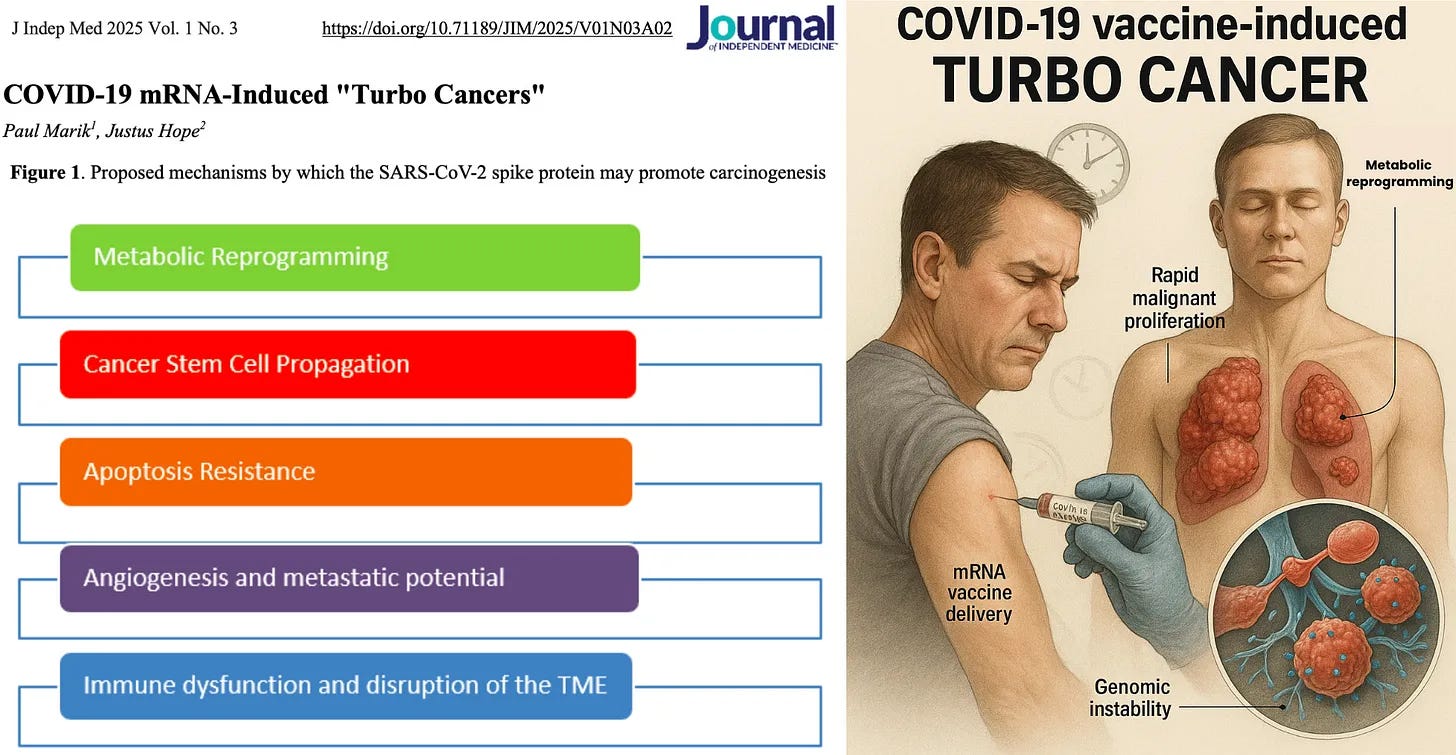

Nicolas Hulscher, MPH·20 AugRead full story
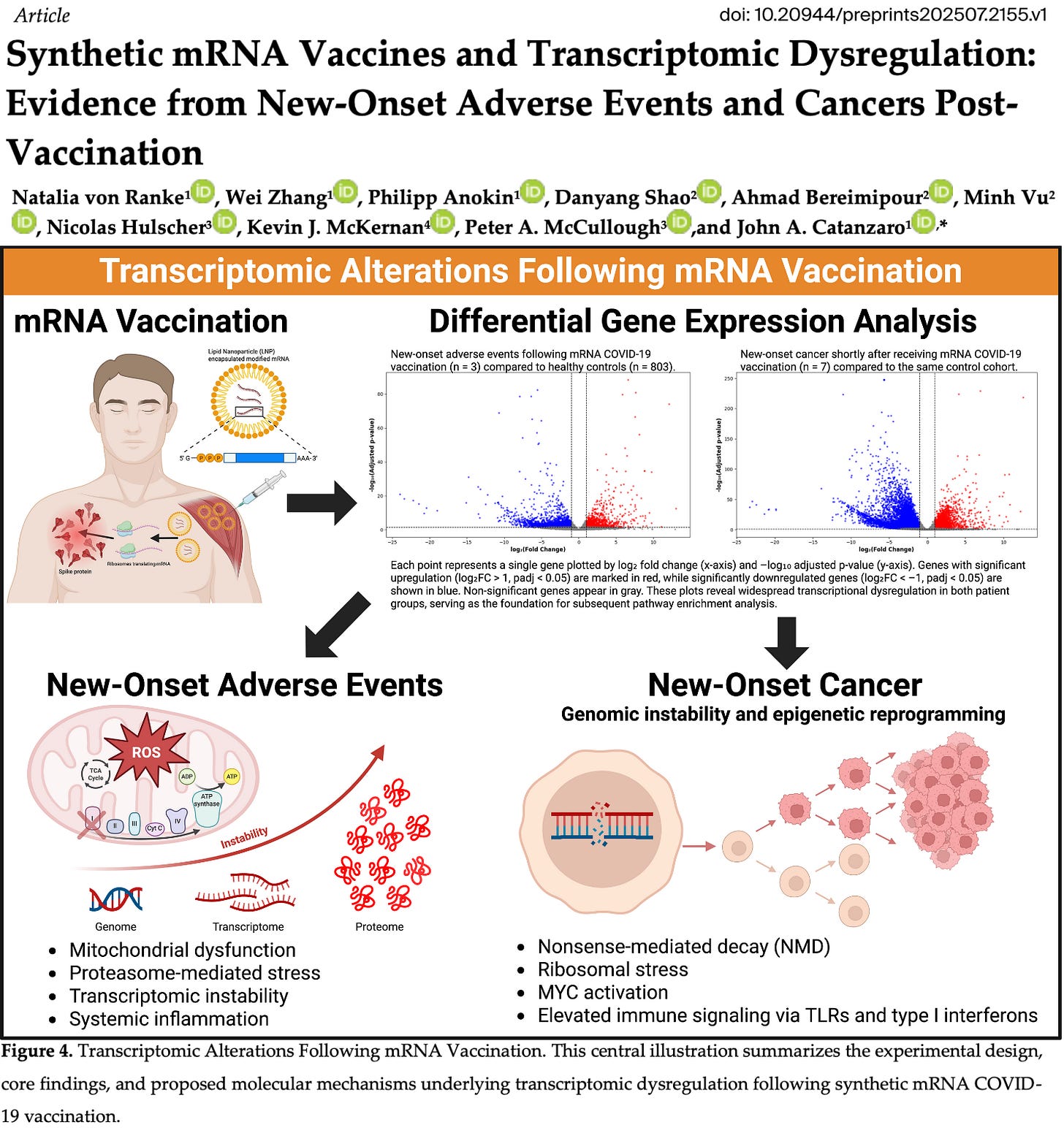
Taken together, these findings form a convergent picture: epidemiologic risk signals, clinical observations of turbo cancers, transcriptomic chaos, and now direct genomic integration in a human subject. This body of evidence supports a biologically plausible framework in which synthetic mRNA vaccines disrupt genome integrity, accelerate malignant transformation, and drive aggressive cancer phenotypes.
While a single case cannot establish definitive causality, the convergence of findings here is undeniable:
These findings demand urgent genomic surveillance, orthogonal validation with long-read sequencing, and large-scale cohort studies to fully assess the genomic and oncologic risks of synthetic mRNA technology.
This evidence compels the immediate withdrawal of all COVID-19 mRNA products from the market. Humanity now confronts the unprecedented threat of vaccine-induced genomic disruption—a danger too great to ignore.
Epidemiologist and Foundation Administrator, McCullough Foundation
Support our mission: mcculloughfnd.org
Please consider following both the McCullough Fo
