 By Independent News Roundup
By Independent News Roundup
Modern cancer policy is dominated by expensive drugs, marginal survival gains, and soaring end-of-life costs. Yet quietly, a low-cost and widely accessible intervention has been sitting in plain sight.
A peer-reviewed analysis published in Molecular Oncology examined what would happen if adults aged 50 and older received routine vitamin D supplementation at modest daily doses. The results are deeply inconvenient for a system built around high-cost treatment rather than prevention.

Using national mortality data and randomized controlled trial meta-analyses, researchers estimated that daily vitamin D supplementation could:
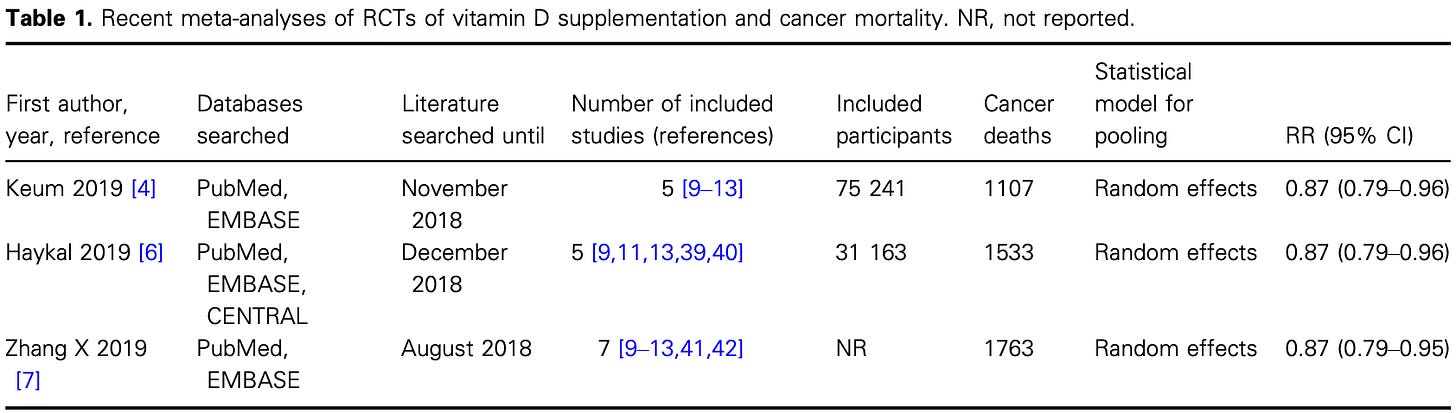
Annual supplementation costs (~$1.0 billion per year) were outweighed by reductions in end-of-life cancer care, producing net savings of ~$280 million annually.
For context, many modern oncology drugs cost tens of thousands of dollars per patient while extending survival by weeks or months. By contrast, vitamin D supplementation:
Even when researchers ignored all cancer-care cost savings, the cost per life-year saved was approximately $3,100 — far below standard cost-effectiveness thresholds used to justify new cancer drugs.
Yet despite widespread deficiency, routine vitamin D supplementation remains absent from most cancer-prevention strategies — while healthcare systems continue to pour resources into late-stage treatment with diminishing returns.
Beyond population-level mortality reductions, a large and growing body of mechanistic, clinical, and translational evidence shows vitamin D activity across multiple cancer types. A 2023 peer-reviewed synthesis of over 900 recent studies highlights consistent anti-cancer effects mediated through vitamin D receptor (VDR) signaling, immune modulation, and tumor microenvironment control.
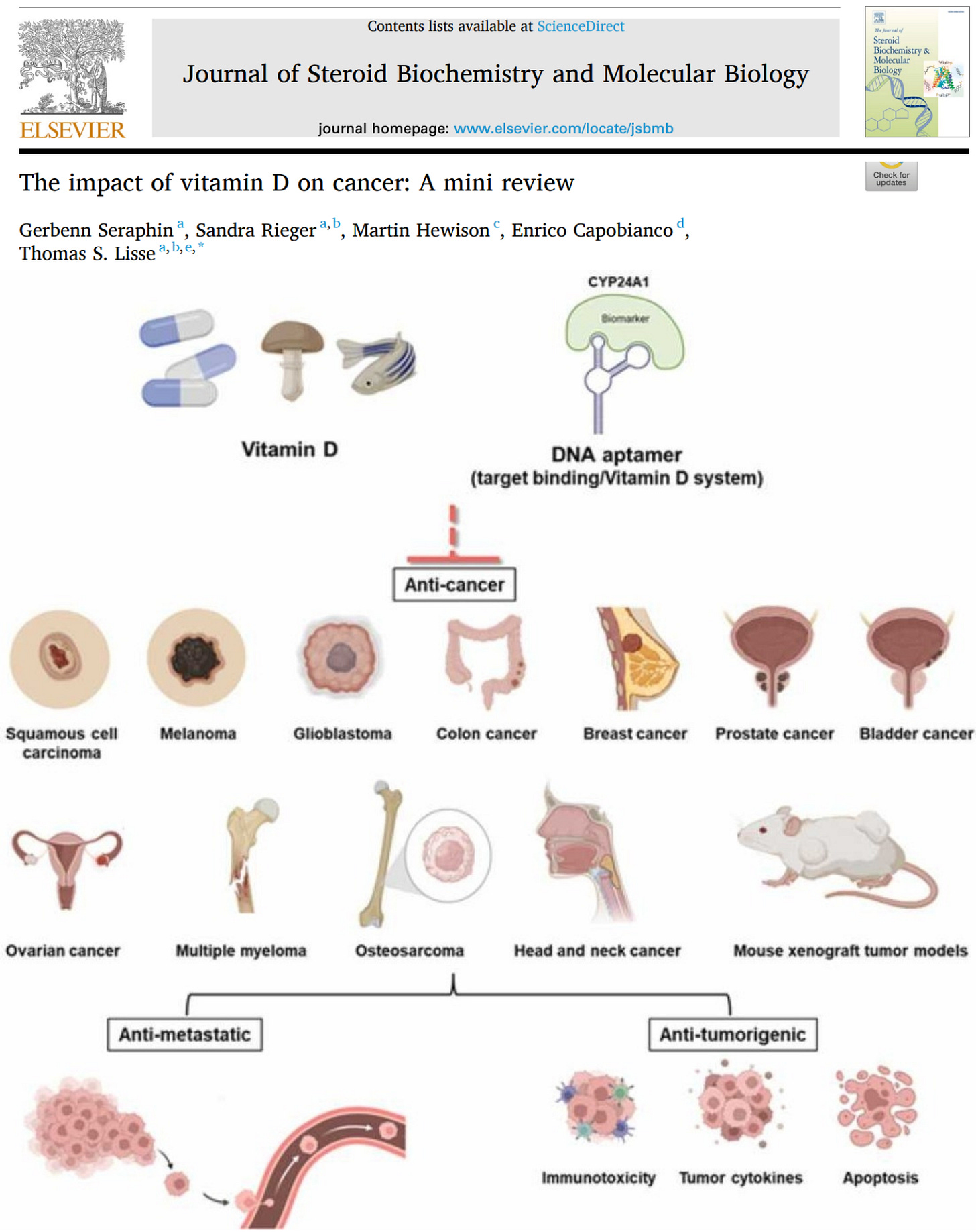
.Vitamin D has demonstrated protective or therapeutic effects in:
Across these cancers, vitamin D has been shown to:
Importantly, low vitamin D status is repeatedly associated with worse prognosis, more aggressive disease, and reduced survival — while adequate levels or supplementation are linked to improved outcomes.
Some of the most powerful cancer-prevention tools are neither novel nor profitable.
Vitamin D is inexpensive. It is biologically active across immune, inflammatory, and cellular regulatory pathways. And according to randomized trial evidence, it saves lives — at scale.
The only real question left is why public health policy continues to ignore it.
Epidemiologist and Foundation Administrator, McCullough Foundation
www.mcculloughfnd.org
